Prevent UIC (under insulation corrosion) with ThinTech coatings, designed to protect your assets against the damaging effects of moisture and harsh environmental conditions.

Introduction to UIC (Under Insulation Corrosion) and Why It’s a Concern for Industrial Facilities
UIC stands for Under Insulation Corrosion, which is a type of corrosion that occurs on the surface of metal pipes and equipment that are covered by insulation materials. This type of corrosion is often hidden from view and can be caused by the presence of moisture, harsh environmental conditions, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations.
Industrial facilities rely on piping systems to transport liquids and gasses, and insulation is often used to maintain temperature and prevent heat loss. However, the insulation material can be prone to corroding pipes, leading to under insulation corrosion.
This type of corrosion occurs when moisture penetrates the insulation and corrodes the pipe underneath, often going undetected until it has caused significant damage. UIC under insulation corrosion can result in equipment failure, safety hazards, and energy loss, making it a significant concern for industrial facilities. Preventative measures, such as proper installation and the use of protective coatings like ThinTech Coatings, can help to reduce the risk of UIC.
Insulation Materials That Are Prone to Corroding Pipes:
Certain insulation materials are more prone to UIC than others. For example:
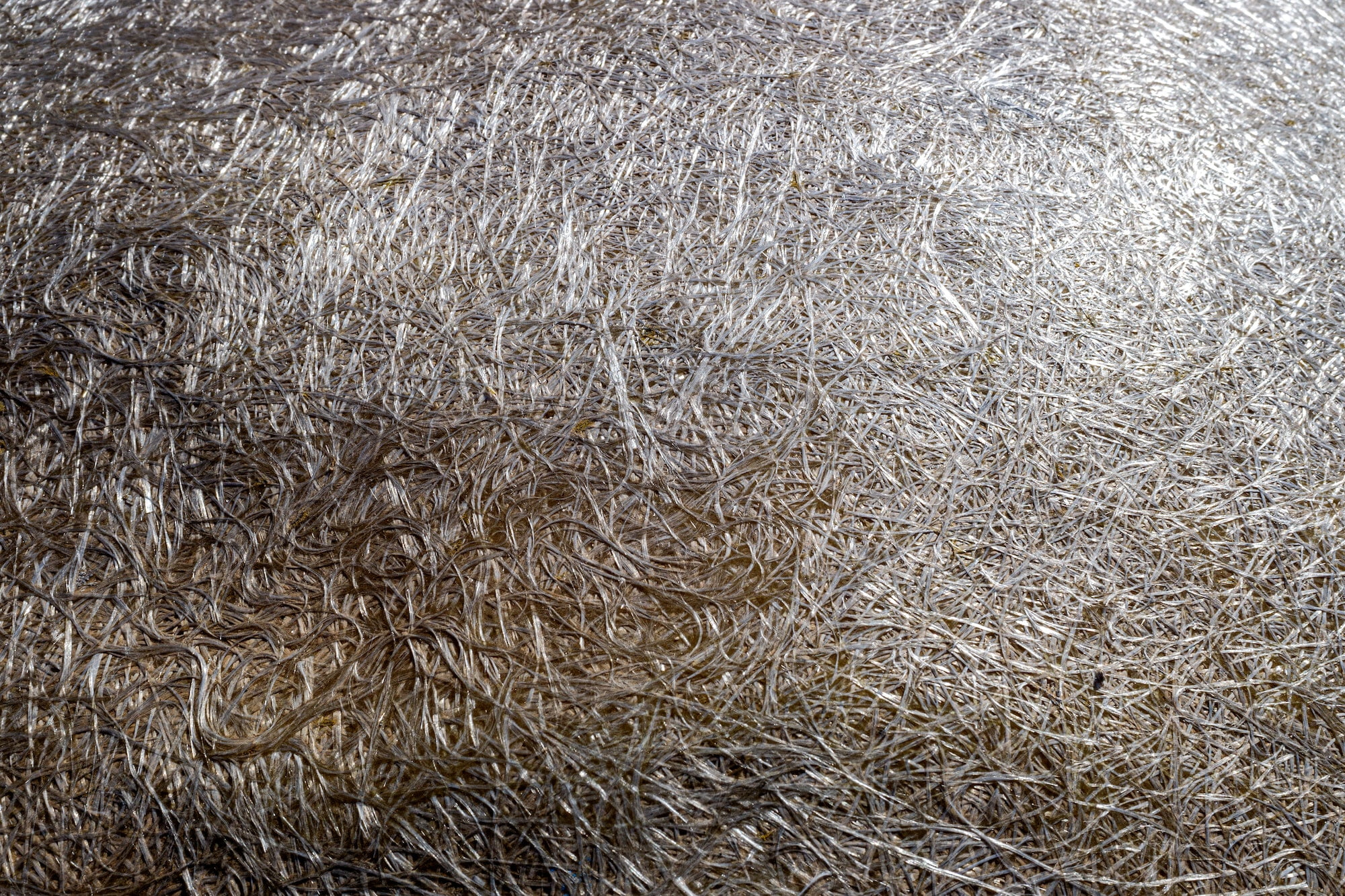

- Fiberglass: Fiberglass insulation is made of glass fibers and is commonly used in industrial facilities. However, it is susceptible to damage to the pipes when exposed to moisture, especially in high humidity environments.
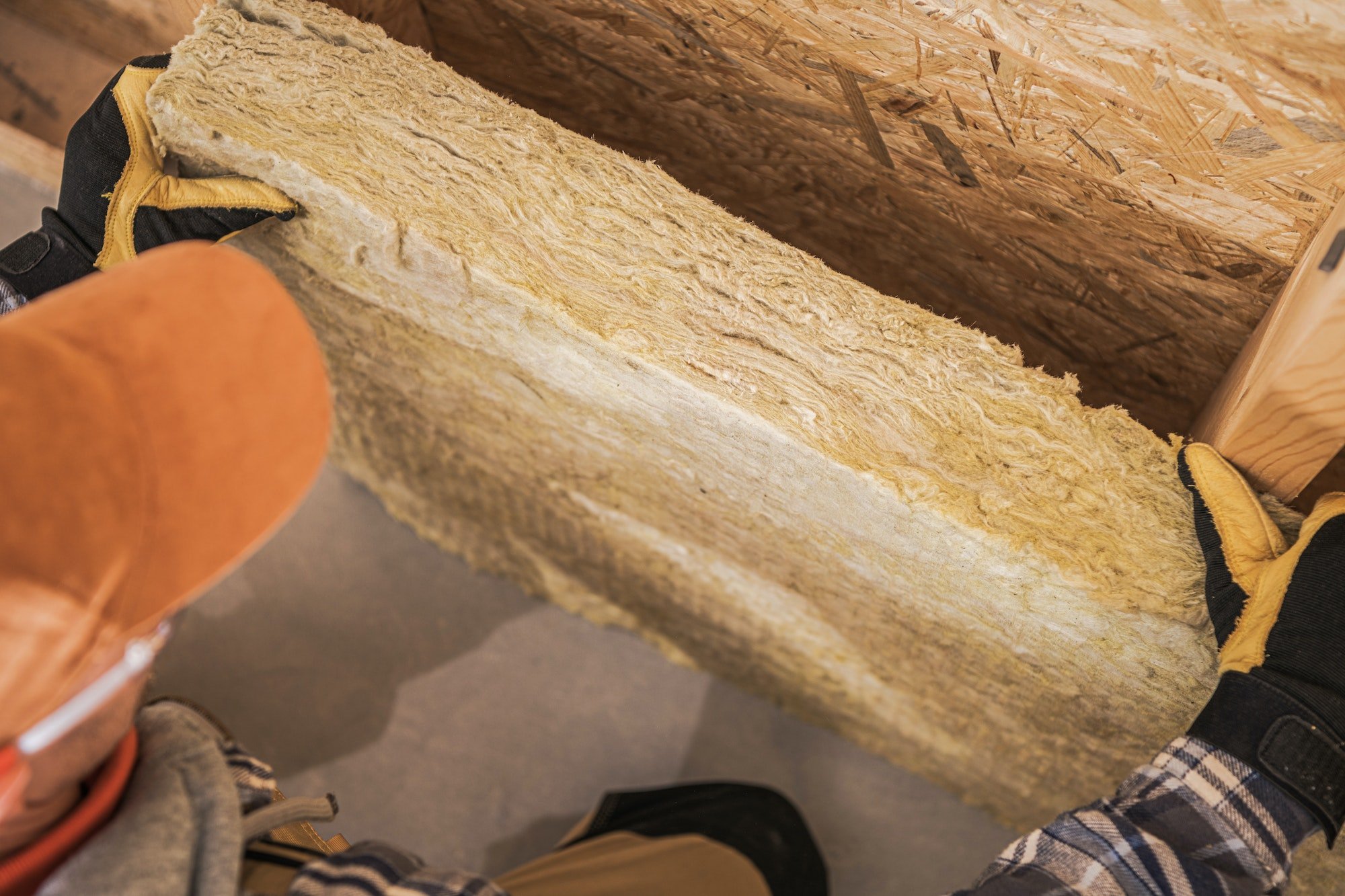

- Mineral Wool: Mineral wool insulation is made from natural or synthetic minerals such as basalt, diabase, and slag. Under specific environmental conditions, corrosion of pipes may occur as well.

- Calcium Silicate: Calcium silicate insulation is made from a combination of calcium, silicate, and reinforcing fibers. It is commonly used in high-temperature applications, but it can also absorb moisture and can release acids that corrode the pipe.

- Cellulose: Cellulose insulation is made from recycled paper or cardboard and is treated with chemicals to make it fire-resistant.

- Polyurethane foam: Polyurethane foam insulation is made by mixing two chemicals that react to create a foam. Exposure to specific chemicals, particularly in industrial settings, increases the likelihood of pipe corrosion.
- Metal jacketing used to protect insulation can also contribute to corrosion if it is not properly installed or maintained.
Understanding the susceptibility of insulation materials to corrosion is important in determining the most suitable materials for specific applications and taking the necessary measures to prevent corrosion from occurring.
Causes of Under Insulation Corrosion, Including Moisture, Harsh Environmental Conditions, Chemicals, and Temperature Fluctuations
Under insulation corrosion can be caused by a combination of factors, including moisture, harsh environmental conditions, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. Moisture can come from humidity, leaks, or condensation, and can penetrate the insulation and corrode the pipe underneath. Harsh environmental conditions, such as exposure to saltwater, can also contribute to corrosion. Chemicals used in the process can be corrosive and accelerate corrosion, and temperature fluctuations can cause expansion and contraction of the pipe, leading to cracks and corrosion.
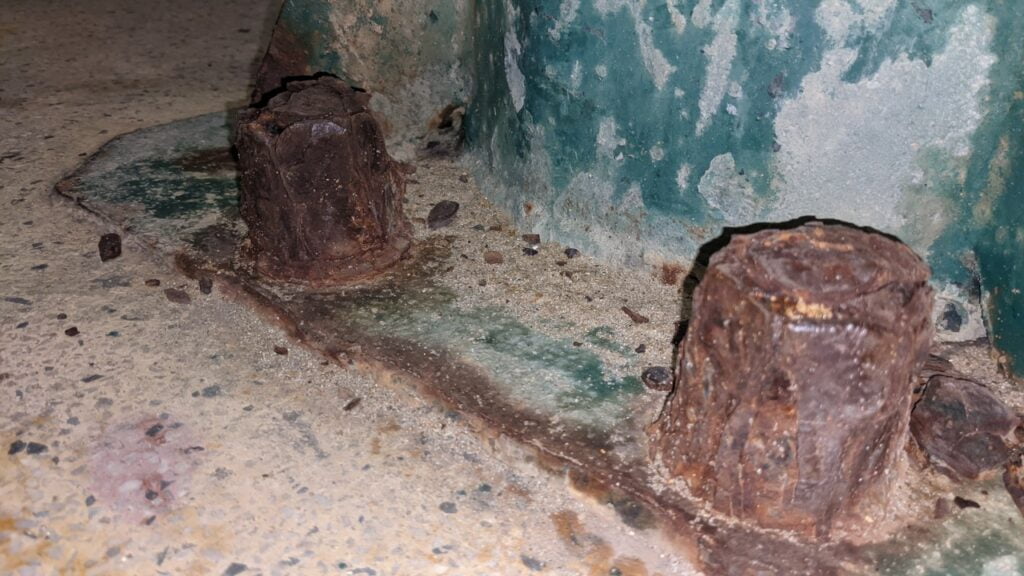

Effects of Under Insulation Corrosion on Equipment, Safety, and Energy Efficiency
Under insulation corrosion can have significant effects on equipment, safety, and energy efficiency. Corrosion can weaken pipes, leading to leaks or bursts that can cause equipment failure or safety hazards. The corrosion can also reduce the efficiency of the piping system, leading to energy loss and increased costs.
Prevention and Treatment Options for UIC, Including Proper Installation, Coatings, and Maintenance
Preventing UIC involves proper installation and maintenance of the insulation and the piping system. This includes using the right type of insulation material and properly sealing it to prevent moisture from penetrating. Coatings, such as ThinTech coatings, can also be applied to protect against moisture and harsh environmental conditions. Proper maintenance, including regular inspections, repairs, and cleaning, can also help prevent under insulation corrosion.
Proper Installation
One of the most effective ways to prevent insulation corrosion is to ensure proper installation. This includes selecting the right insulation materials for the environment, ensuring a tight seal to prevent moisture penetration, and avoiding gaps or spaces that could trap moisture or contaminants. Additionally, proper installation techniques should be followed, such as using appropriate fasteners and sealants to prevent air leaks and moisture ingress.
Coatings
Applying coatings to insulation materials can provide an additional layer of protection against corrosion. For instance, ThinTech coatings can be applied to a variety of insulation materials to provide resistance against moisture, chemicals, and other corrosive substances. These coatings also help to improve energy efficiency by reducing heat loss, which can lead to lower energy costs and increased sustainability.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance and inspections can help detect insulation corrosion early and prevent further damage. Insulation should be checked periodically for signs of damage, such as cracking or peeling, and any issues should be addressed promptly. Additionally, insulation should be kept dry and clean to prevent corrosion from moisture or contaminants.
Replacement
In some cases, insulation may be too damaged to salvage and will need to be replaced. When replacing insulation, it’s important to select materials that are appropriate for the environment and follow proper installation techniques to prevent future corrosion. It’s also essential to consider the cost-benefit analysis of replacement versus repair, taking into account the long-term benefits of preventing insulation corrosion.
Case Studies/Examples of Successful UIC Prevention and Treatment
Several industrial facilities have successfully prevented and treated UIC using coatings such as ThinTech coatings. For example, a chemical plant in Texas applied ThinTech coatings to prevent corrosion in their piping system, resulting in a significant reduction in maintenance costs and improved safety. A power plant in Pennsylvania also used ThinTech coatings to protect against corrosion and extend the lifespan of their piping system.
Conclusion
In conclusion, UIC (under insulation corrosion) can have significant impacts on industrial facilities, but prevention and treatment options are available. Proper installation, maintenance, and the use of coatings such as ThinTech coatings can help prevent UIC and protect against the damaging effects of moisture and harsh environmental conditions.